Ubiquitin Phosphorylation as New Signalling System in Chromatin Biology
Background
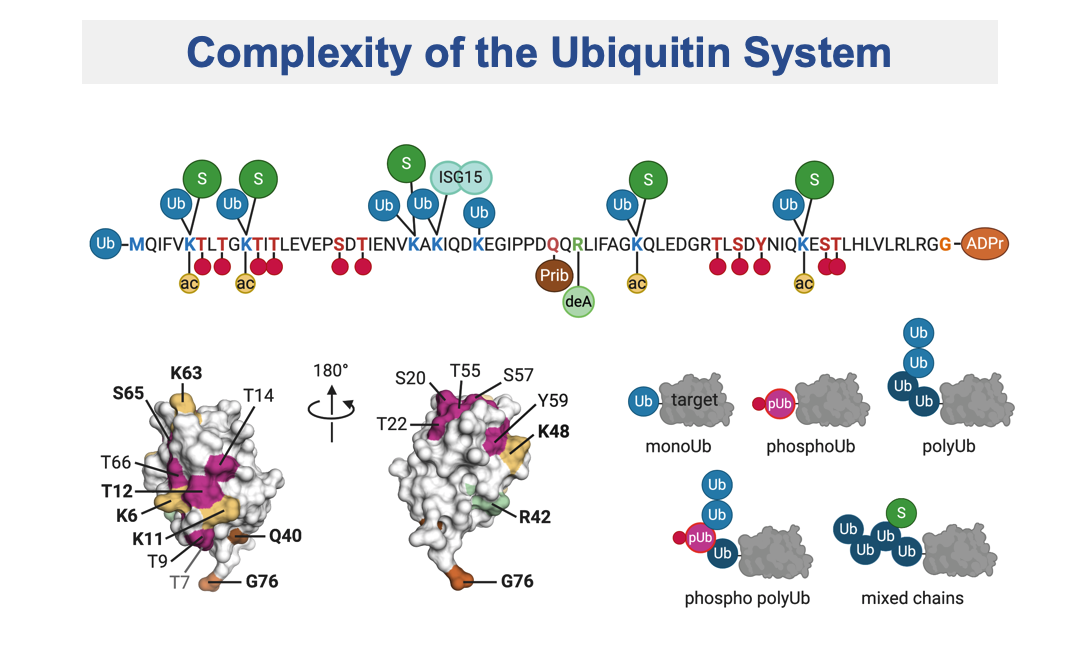
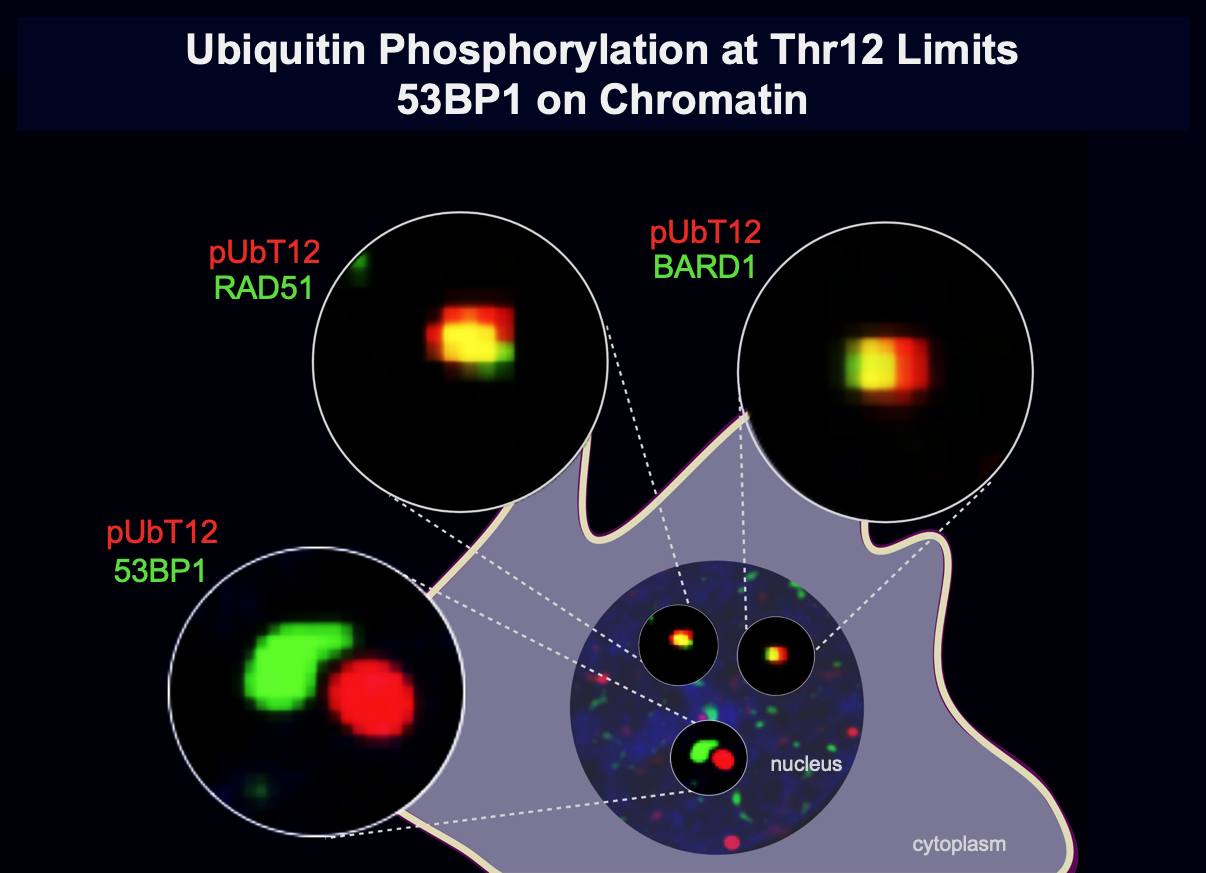
Maintaining genome stability is crucial for all living cells and organisms. The repair of the highly cytotoxic DNA double-strand breaks is based on a variety of factors that modify chromatin structure, such as kinases and ubiquitin ligases. Our previous studies demonstrated that H2AK13ub/H2AK15ub promoted by RNF168 is a key event in this pathway. However, how the RNF168 pathway is functionally implicated in determining the type of DNA repair to promote, either the NHEJ – via 53BP1 – or the HR – via BRCA1 – is still missing. Aiming at understanding how H2AK15Ub governs this decision, we recently found that a key event is the phosphorylation of ubiquitin, quite a new concept in the ubiquitin field, at Thr12 (pUbT12). pUbT12 turned out to be an essential regulator of the DDR signalling cascade, by preventing the recruitment of 53BP1 to damaged chromosomes, with potential implications in the DNA repair pathway choice.
Goal
Investigating the dynamics of pUbT12 modification on chromatin, by identifying the players involved in this novel pUb-based signalling system.
Ongoing and future work
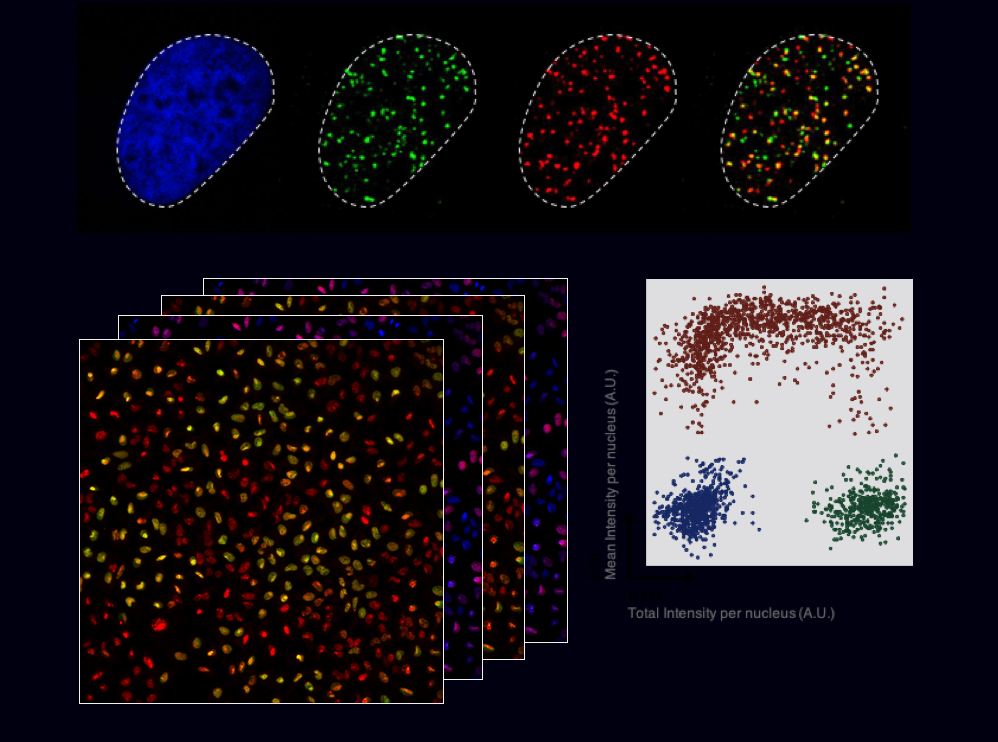
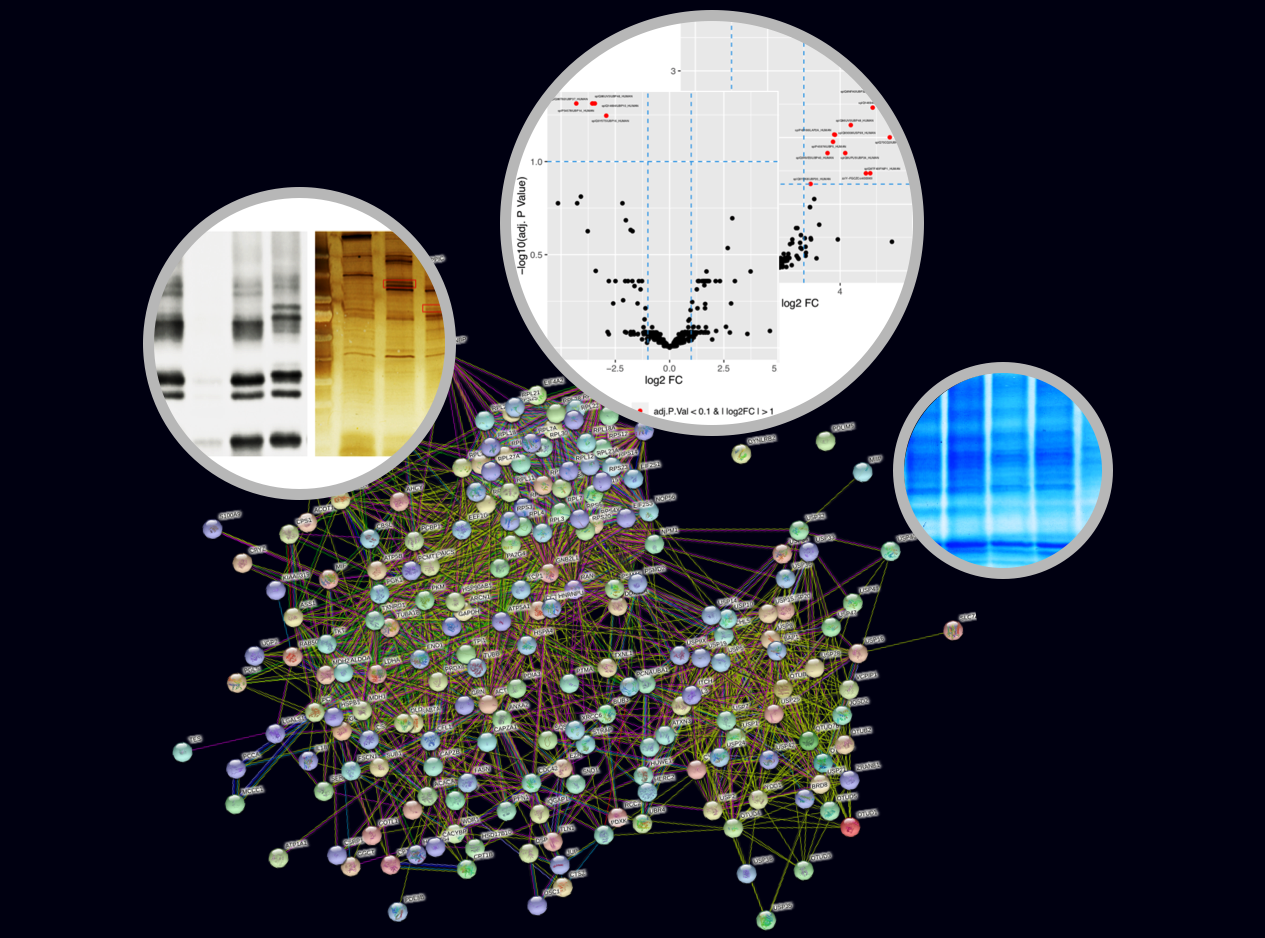
Modification of ubiquitin by small chemical groups affects surface charge and structure properties, often resulting into functional alterations of its conjugation, deconjugation and interaction properties. By combining state-of-the-art techniques, we are currently investigating the regulators of this ubiquitin phosphorylation i.e., the writers (ubiquitin kinases), the erasers (phospho-DUBs) and readers (proteins carrying phospho-ubiquitin binding domains). This will help understanding how this phosphorylation affects the chromatin landscape, by driving the recruitment of different yet-unknown factors, and what are the biological consequences of it.
Selected publications
Mattiroli and Penengo L. Histone ubiquitination: an integrative signaling platform in genome stability. Trends in Genetics (2021).
Walser F, Mulder M, Bragantini B, Gatti M, Gubser T, Burger S, Botuyan MV, Villa A, Altmeyer M, Neri D, Ovaa H, Mer G, Penengo L. Ubiquitin Phosphorylation at Thr12 Modulates the DNA Damage Response. Molecular Cell.
Penengo L, Mapelli M, Murachelli AG, Confalonieri S, Magri L, Musacchio A, Di Fiore PP, Polo S, Schneider TR: Crystal structure of the ubiquitin binding domains of rabex-5 reveals two modes of interaction with ubiquitin. Cell (2006).